Imagine the pain of going through the complete document over and again to find the key information. Wouldn't it have saved a great deal of time and energy, had the important keywords and data singled out separately in the book with the page numbers on it? This work is called indexing in the publication process and treated as a final draft. It is executed at the end of the publishing process along with proofreading.
Indexing refers to cross-examine of facts like names, titles, places, scientific terminology, publication dates, and analyze italicized words contained in the written text. The readers find it easy to access relevant data after indexing in alphabetical order. We generally find the index on the last few pages of the book.
Index is created after proofreading and finalizing the page proofs. The readers while reading a book, use the index as reference tool to direct to the concepts and key content. Although publication indexing concentrates only on important terminologies and data in the book, focus is more on pointing out significant relevant information. We see this mostly in research books as well as non-fiction writing while most fiction books do not cover indexes.
How is Publication Indexing covered?
Publication Indexing requires sharp eyes to produce the necessary information that matches the pages listed in the book. Abstracting and Indexing Service makes it easy to search in the database of the product and is carried out at the same stage when the final proofreading is underway. Most Publishing Houses keep Abstracting and Indexing services available to the writers. It is significant for the author to approve of the changes suggested by the editor for indexing.
Few steps on how to do publication indexing:
- Rough Indexing starts with preparing a list of titles and subtitles with their location for relevant reference.
- After completing rough indexing, the document is again scrutinized to edit for clarity, structure, specifications maintained, consistency checked, and proofread which is then sent to the client as the final draft. In this stage, we check for capitalization and italicization in the texts and correct them wherever applicable.
- The length of the document decides the time taken for publication indexing. The lengthier the copy is, it will take more time to index it.
- Index contains extra features like images, illustrations, graphics, charts, figures, formulas, scientific derivations, and tables because these data also contain important information .
- Although page proof creation and the titles matching the index, the only work left is adding page numbers in the draft that will make it ready for printout. Client approval is important for the indexer to further the work.
The editor will review these corrections again that include copy editing and revising the index to check style consistency. The content will then integrate all the additional and missing parts suggested by the editor after which, will be ready for final proofreading.

5 Steps to publication indexing
Indexing turns out to be fun if you have the knack for reading everything that comes to your hand. The more you read, the better you understand the purpose of indexing. How do we know that an index is good? A clear and detailed index serves its purpose.
Tips to index your book
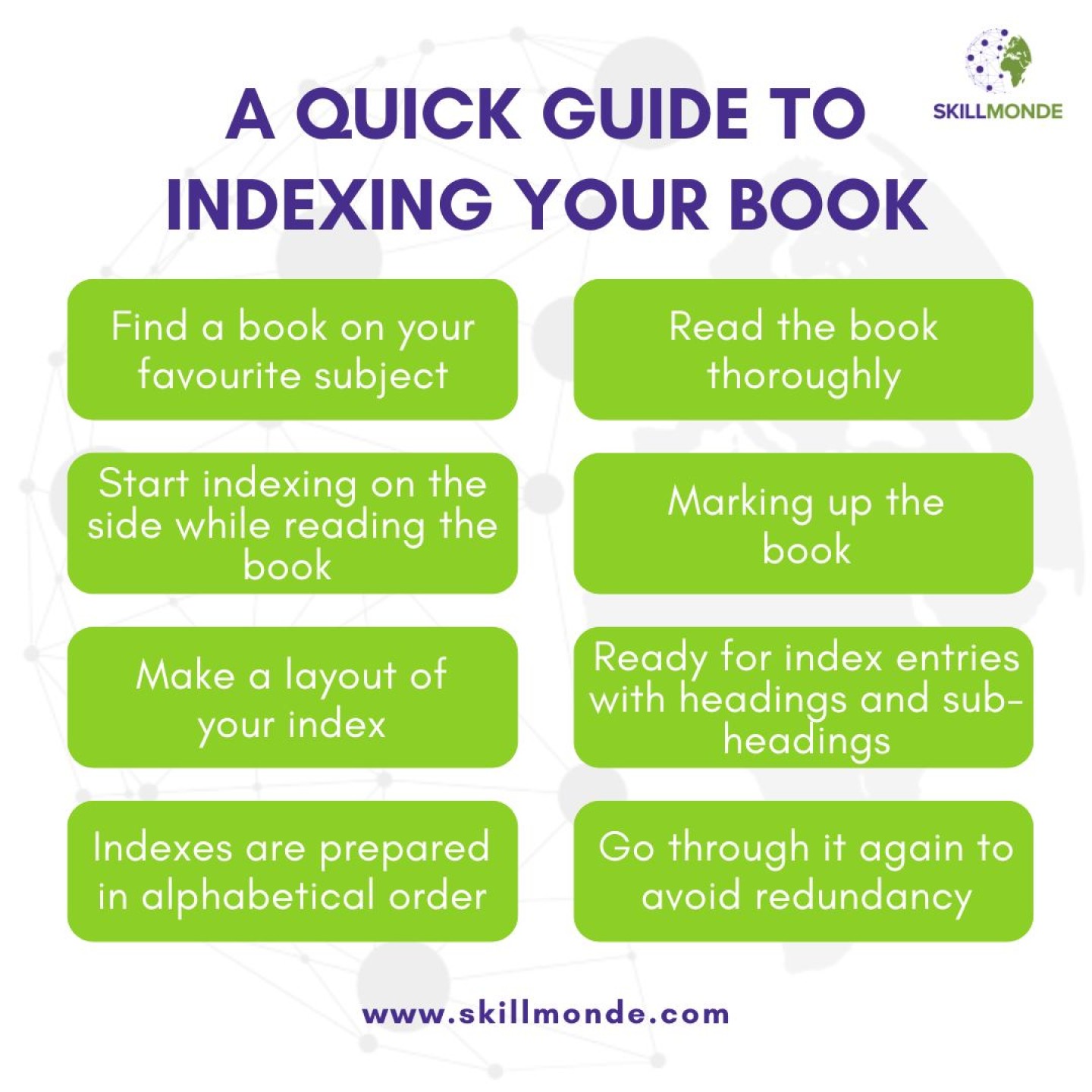
For beginners who are thinking to give indexing a shot, here are a few tips to start with:
-
- Find a book on your favorite subject that you want to start the work of indexing with. You better choose an interesting topic to read for the job before reading puts you to sleep.
-
- Good indexing requires thorough reading. Besides reading the book once, it is equally important to read it again carefully for indexing because such a process is necessary for proper indexing.
-
- You can start indexing on your second reading, only after an exhaustive reading, .
-
- There are many indexing software available in the word processor. This is an option that you may want to use as a starter.
-
- The next step is marking up the book. Identify all the important topics and terminologies in the article. This will prepare the list of keyword and key content in the index.
-
- Index layout and writing are the next things to pick to maintain style guide consistency throughout.
-
- After a thorough examination of all the discussions above, the next step in line is ready for index entries with headings and sub-headings.
-
- Indexing usually follows alphabetical order.
-
- Check for repetitions and redundancy in the entries after completing the first drafting. Make necessary corrections after which your final draft is ready for submission.
You can always master the art of indexing if you can devote your time to reading and develop the practice of finding the important topics in it.
FAQs
- What does publishing indexing actually mean?
- Publication indexing includes adding publications to a database for the publishers to trace their work, much like a search engine.
- Why is indexing important in publication?
- Publication indexing makes it easier for readers to locate and access information which, in turn boosts the impact and visibility of the research.
- Which popular databases index publications are there?
- Other well-known databases that index papers include are - PubMed, Scopus, Web of Science, Google Scholar, and Directory of Open Access Journals (DOAJ).
- How to index my work?
- Indexing of articles varies depending on the indexing database. However, in general, it comprises submitting your piece to the database and ensuring that it meets the conditions for inclusion.
- What are the important points to remember as an indexer?
- To index your publication, you need to -
-Use pertinent keywords in your title and abstract
-Make sure your piece is well-written and of high quality
-Promote it on social media and other platforms.
- How much time does it take to index a book?
- It may take from a few days to many months, depending on the indexing database and other factors.
- What is the average earning of a publication indexer?
- The salary of an Indexer ranges between 1 lakh and 4 lakhs annually. This largely depends upon the expertise, skill and time of the individual in the industry.
- What are some typical explanations to not index a publication?
- Reasons why a publication might not be indexed are - not satisfying the requirements for inclusion in the indexing database, not being written in the database's preferred language or format, or being published in a low-quality or predatory journal.