Conversion and Digitisation: The publishing industry is constantly evolving. With the technology ever advancing, the publication process is slowly and gradually adopting the digital method. To reach more readers and stretch the length of the audience globally, the process of publication is undergoing the method of conversion and digitisation.
There was a time when parents bought printed books for their children to read and learn from. Now is the age when parents buy electronic devices for their children for learning and knowledge. We find everything online. All we need to do is look up.
Print publications are taking backseats and online platforms are taking over the publication market. Having said so, there is still a section of people who prefer books over electronic devices and traditional print publication is continuously serving them.
Writing is slowly taking digital forms where there are a greater number of readers. Electronic devices like IPads, tablets, Kindle and mobile phone cater to readers from different backgrounds that prefer online services.
Conversion and Digitisation are also applicable to the resources found in libraries. This technology preserves the resources and makes them easily accessible to the readers. Digitisation has eased the task of retrieving information from anywhere in the world.
What are Conversion and Digitisation?
The process that involves the conversion of audio, pictures, and handwritten texts into a machine-readable format is called conversion and digitisation. Conversion and digitisation are interchangeably used as both refer to the transformation of textual data into digital information.
Optical Character Recognition (OCR) is a tool that extracts numbers and words from images and presents them in digital texts. Scanning is another technique that scans images and presents them to the computer screen.
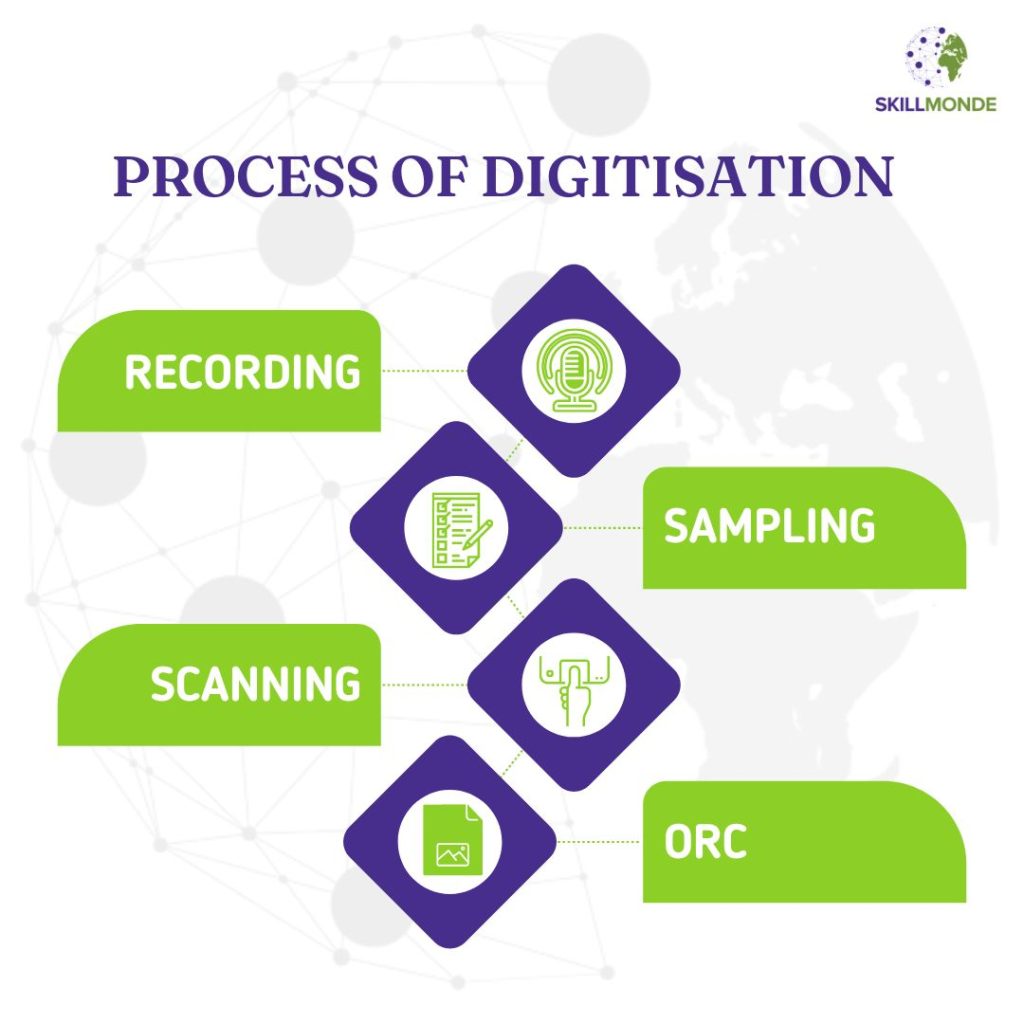
The process of digitisation involves the following processes:
· Recording
· Sampling
· Scanning
· OCR.
Types of data or information that can undergo digitisation are videos, audios, images, texts and numeric data. There are different Data Conversion Techniques by which printed copies can be converted into digital content.
Besides converting printed data into digital forms like e-Pub, XML word, this conversion technique refers to data evaluation, analysis and conversion planning. Publishers are now emphasising more on digital format as this is the new trend among learners.
To optimise information for digital platforms and guarantee its availability across many platforms, educators are cooperatively collaborating with governments and local authorities.
Pros and Cons of Digitisation:
Some merits works wonder but there are demerits also that pose a threat to the publishers. The merits are-
· Digital information becomes easy to share, save and get access from any electronic medium.
· It saves a lot of time as the data is available with just one click on the internet and on electronic devices.
· It gets easier to manipulate digital information and use it to analyse the quality of learning effectively.
· Digitisation does not require the usage of ink, and paper for print which was evident in the traditional printing process. It helps the publishing house from spending extra money.
· It boosts the efficiency of smooth operation.
· This method is more of meeting deadlines and takes less time than the printing process.
· It optimises workflow management.
The demerits of digitisation are not many but touch a few concerning points that result in loss for the publishing companies-
· Easy to copy and distribute illegally which results in loss-making business for the publishing houses. Easy access may end up in piracy in this business.
· Online works seldom seek copyright holders’ permission and end up copying the original work on different platforms in no time. It has become easy and fast for piracy.
· It is easy to change, alter and delete digital information which may witness flashing incorrect data which is taken up without proper research and identification.
Conversion and Digitisation in Education Sector
Digital format is the next big thing in the education sector. Many learning institutes and universities are adopting digital platforms to educate students, present seminars, and conduct classes using tools like PowerPoint Presentation, HTML, XML, and other technology.
The Course Management System (CMS) is increasingly used in learning and teaching programs. CMS optimises students’ attention and focus in the notes, study materials and class works supplied by the teachers.
Educators are more inclined towards CMS. It promises a better future for the students. The Learning Management and Homework Management system strives to optimise the standard of education and focus on the improvement of the student’s learning capacity by reducing the workload on students and frequent changes of content that leave the students in confusion.
Data Entry Operations using Digitisation
Every company, organisation, and educational institution maintains a registry of everything to have easy access and knowledge of the company’s work. These are data and information that go on record. Data is entered and maintained for effective workflow in an organisation.
This is also digitising handwritten notes and texts in printed form into digital format. Only texts are involved in this service. Images are not included in data entry operations. Information is stored in a system like computers, laptops, etc.
What is the process?
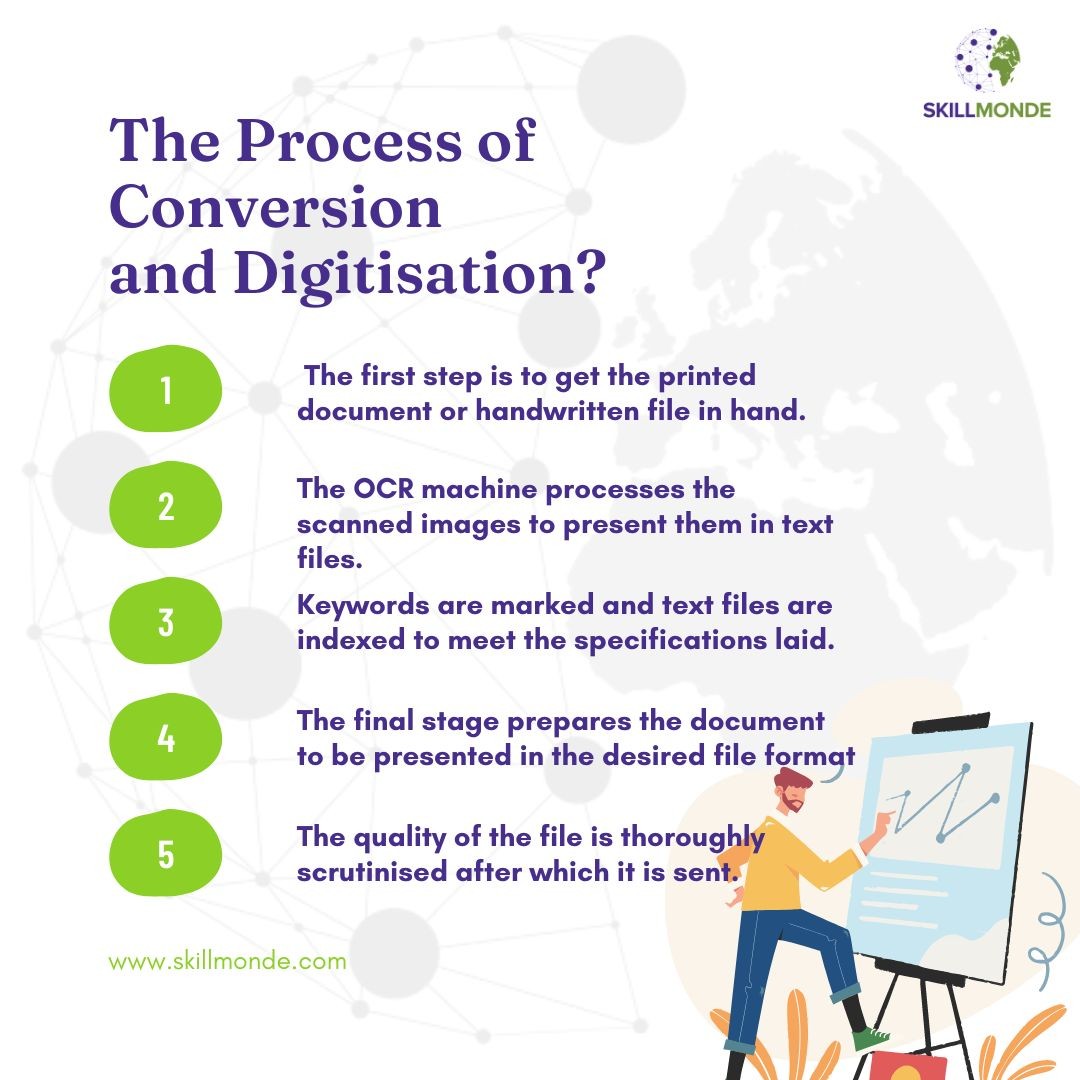
Document conversion and digitisation undergo different stages to see the content on the screen. Following are the steps of conversion and digitisation of information:
1. The first step is to get the printed document or handwritten file in hand. After scanning these documents, they are converted into image format.
2. The OCR machine processes the scanned images to present them in text files. The text files are cross-checked to match with the original file received and check that all the details are included in the text files.
3. Keywords are marked and text files are indexed to meet the specifications laid down by the client. This stage is important because it rates the quality of the work.
4. The final stage prepares the document to be presented in the desired file format as specified by the client.
5. The quality of the file is thoroughly scrutinised after which it is sent to the email id of the client. DVDs, hard-disk drives, CDs, and other storage media are used to store the formatted file.
A large volume of contents are converted into a digital-friendly format that can be easily accessed and used for learning, teaching, and gaining knowledge. Digitisation is changing the face of the publication process which is widely implemented to break the barrier walls of communication.
FAQs on Conversion and Digitisation
1. How does conversion work?
Answer: Conversion is the process of converting data or information from one format to another. For instance, changing a paper document into a digital one, like a PDF and other digital formats.
2. Describe digitalization.
Answer: Digital information can be accessed and processed by computers when analogue information, such as tangible documents or photographs, is transformed into digital form.
3. What makes digitization crucial?
Answer: Information is easier to access, search for, and distribute thanks to digitization. Also, it makes it simpler to preserve and safeguard significant historical and cultural artefacts.
4. What advantages does digitalization offer?
Answer: Digitization can improve information access, save on storage expenses, and free up space. Also, it helps increase the speed and accuracy of data processing and analysis.
5. How can I convert the paper documents I have?
Answer: Paper documents can be digitalized in a variety of methods, such as by utilising a scanner, a digital camera, a smartphone, or a document conversion service.
6. Describe OCR.
Answer: The technology known as OCR, or optical character recognition, enables computers to read and recognise text in scanned documents or photographs.
7. Describe metadata.
Answer: Information that describes the content, context, or structure of data is known as metadata. It may contain information about a digital file's author, date, title, and keywords.
8. How should I set up my digital files?
Answer: Creating a logical organisational structure, naming files consistently, and utilising metadata to tag and categorise files are all part of organising digital files. Software tools are also accessible that can aid in automating the organisation process.
9. How can I make sure that my digital files are secure?
Answer: You should periodically back up your digitised information, employ encryption and strong passwords, and limit access to sensitive files to keep them secure. Using dependable antivirus and security software is essential for defending against malware and online threats.